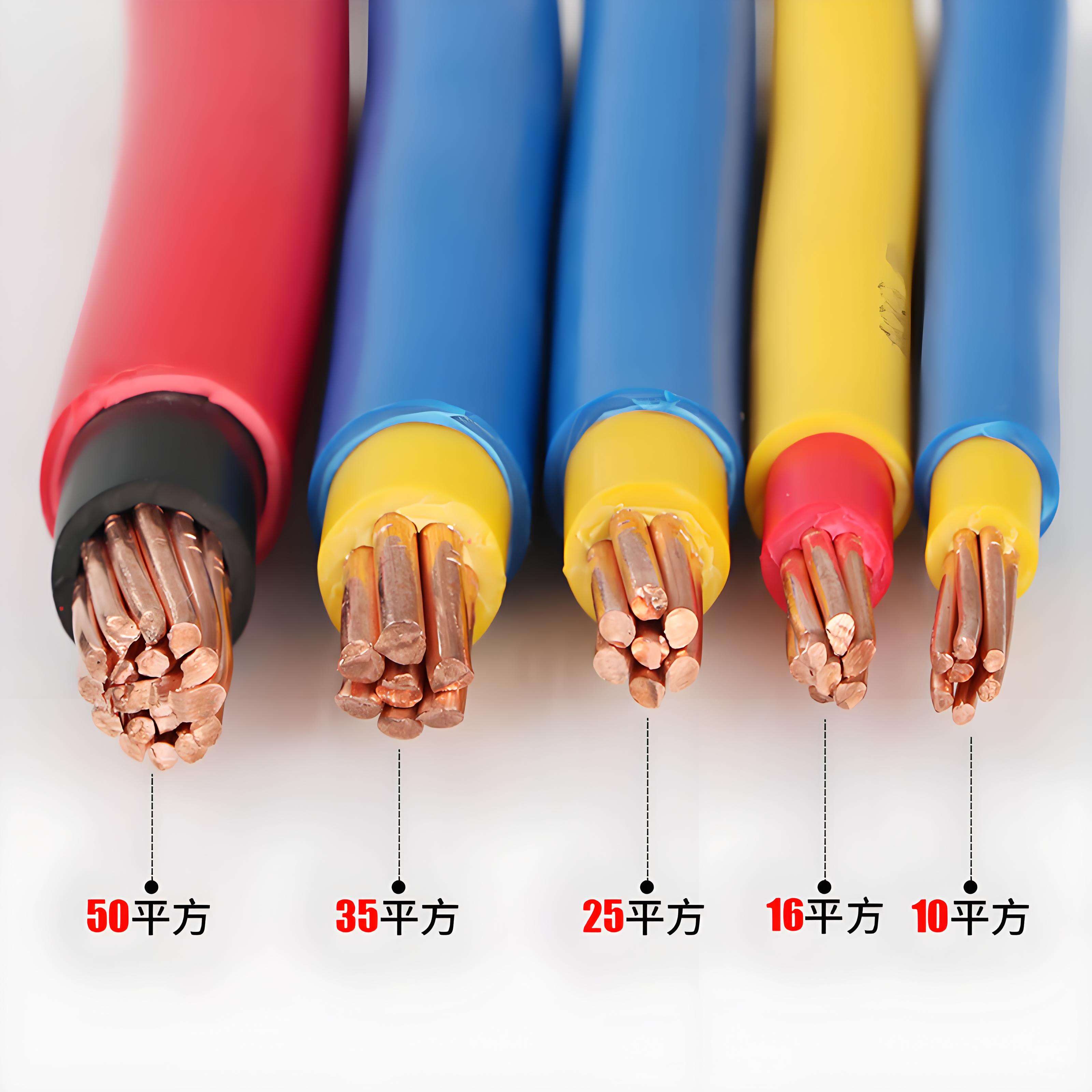
Electrical wires come in a diverse range of types, each designed to meet specific electrical and environmental requirements. One of the most common types is the single-strand wire, which consists of a single solid conductor. These wires are typically used in applications where flexibility is not a primary concern, such as in fixed electrical installations within buildings. Multi-strand wires, on the other hand, are made up of multiple small conductors twisted together, offering greater flexibility and are often used in applications where the wire needs to be bent or moved frequently, like in appliances or portable electronics. Copper wires are widely used due to their excellent electrical conductivity, while aluminum wires are sometimes preferred for their lower cost and lighter weight, especially in large-scale power distribution systems. Insulated wires are essential for safety, as the insulation layer prevents electrical current from leaking and protects against electrical shock. Different insulation materials, such as PVC, XLPE, and rubber, offer varying levels of heat resistance, durability, and chemical resistance, making them suitable for different environments. Shielded wires are designed with an additional layer of shielding material, usually a metal braid or foil, to protect against electromagnetic interference, making them ideal for applications involving sensitive electronic equipment. Additionally, there are specialized wires like coaxial cables used for transmitting radio frequency signals, and fiber optic cables that use light to transmit data at high speeds, expanding the range of electrical wire types available for different communication and electrical needs.