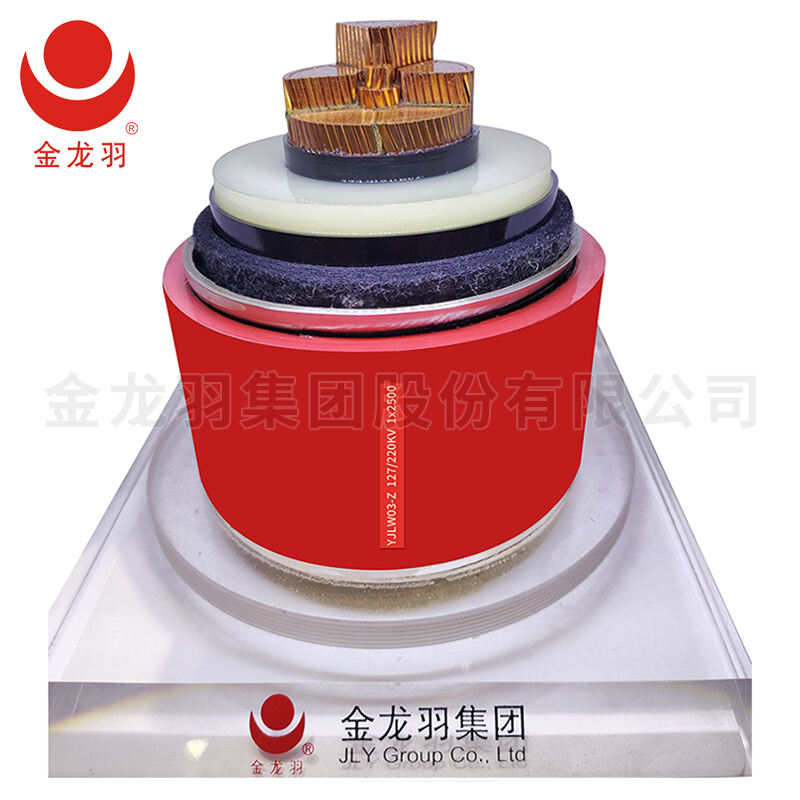
Biết cách kiểm tra cáp điện là yếu tố thiết yếu để xác minh hiệu suất, an toàn và độ tin cậy của chúng trước và sau khi lắp đặt, và Weidong Technology khuyến nghị các quy trình này dựa trên các tiêu chuẩn ngành. Phương pháp đầu tiên trong cách kiểm tra cáp điện là thử nghiệm độ dẫn thông mạch, sử dụng đồng hồ vạn năng để kiểm tra xem dòng điện có chạy qua dây dẫn hay không, đảm bảo không có chỗ ngắt – điều này rất quan trọng đối với cáp cấp điện và cáp tín hiệu. Khi tìm hiểu cách kiểm tra cáp điện, thử nghiệm điện trở cách điện bằng thiết bị megohmmeter sẽ đo điện trở giữa dây dẫn và đất, phát hiện các điểm rò rỉ có thể gây ra chập mạch hoặc điện giật, kết quả sẽ được so sánh với thông số kỹ thuật do nhà sản xuất cung cấp (ví dụ như các thông số từ Weidong). Một bước quan trọng khác trong cách kiểm tra cáp điện là thử nghiệm điện áp, áp dụng điện áp định mức để kiểm tra sự đánh thủng cách điện, đảm bảo cáp có thể chịu được áp lực vận hành mà không bị hư hỏng. Đối với cáp điện áp cao, cách kiểm tra cáp điện còn bao gồm thử nghiệm phóng điện cục bộ để phát hiện các khuyết tật bên trong có thể trở nên nghiêm trọng theo thời gian. Ngoài ra, việc kiểm tra vật lý cũng là một phần trong cách kiểm tra cáp điện, nhằm phát hiện hư hại ở lớp cách điện, vỏ bọc hoặc đầu nối. Bằng cách thực hiện các phương pháp kiểm tra cáp điện như trên, người dùng có thể đảm bảo cáp đáp ứng các tiêu chuẩn chất lượng và hoạt động ổn định trong các ứng dụng dự kiến.