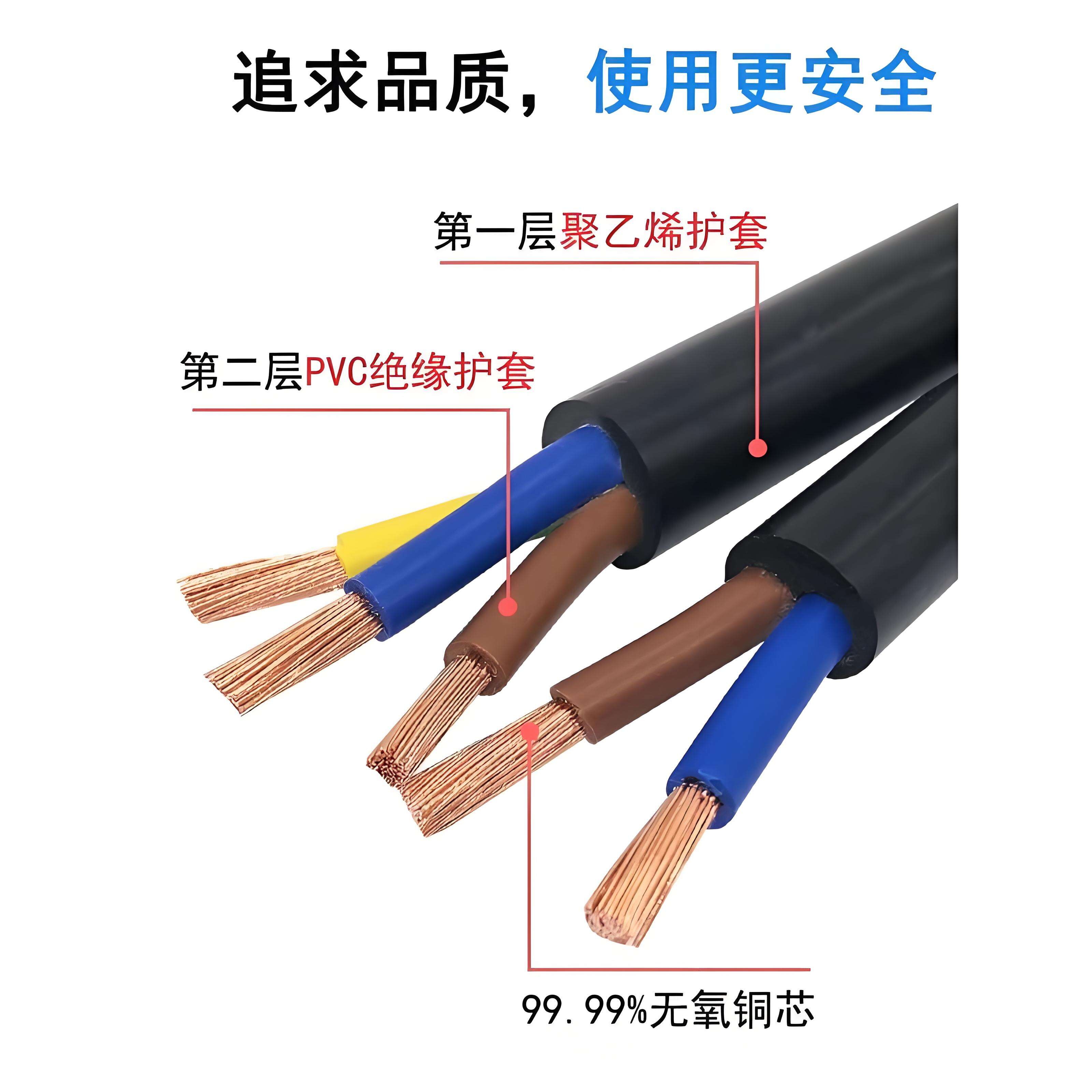
Quality standards for electrical wires are established to ensure safety, reliability, and optimal performance in electrical systems. These standards govern various aspects, starting with the conductor material. High-quality electrical wires typically use oxygen-free copper or high-purity aluminum conductors, which offer excellent electrical conductivity and resistance to corrosion, minimizing power loss and ensuring stable current flow. Insulation materials are also strictly regulated; materials like cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), or low-smoke halogen-free (LSZH) compounds must meet specific criteria for electrical insulation, mechanical strength, and fire resistance. For instance, flame-retardant insulation is mandatory in many regions to prevent the spread of fire in case of electrical malfunctions. Additionally, quality standards cover wire gauge, which determines the wire's current-carrying capacity, and proper labeling, ensuring that information such as voltage ratings, conductor material, and insulation type is clearly and accurately indicated. Regular testing by accredited laboratories, including insulation resistance tests, tensile strength tests, and flame spread tests, verifies compliance with these standards, guaranteeing that electrical wires meet the necessary quality benchmarks for diverse applications.